Sustainable Coffee Production: Why Your Coffee Choices Matter

In today’s world, the choices we make as consumers hold immense power. Among these decisions, how we enjoy our coffee can significantly impact the environment, communities, and economies worldwide. While that morning cup of coffee provides comfort and energy, it’s essential to consider where that coffee comes from and how it’s produced. Sustainable coffee production is not just a trend—it’s a movement that we, as consumers, can actively contribute to, protecting the future of coffee and the planet.
This blog will explore sustainable coffee production, why it’s essential, and how your coffee choices can contribute to a more sustainable world.
What Is Sustainable Coffee Production?
At its heart, sustainable coffee production aims to ensure that coffee is grown, harvested, and processed in environmentally responsible, socially equitable, and economically viable ways. This holistic approach means that everyone involved in the coffee supply chain—from farmers to consumers—benefits without sacrificing the future of our planet.
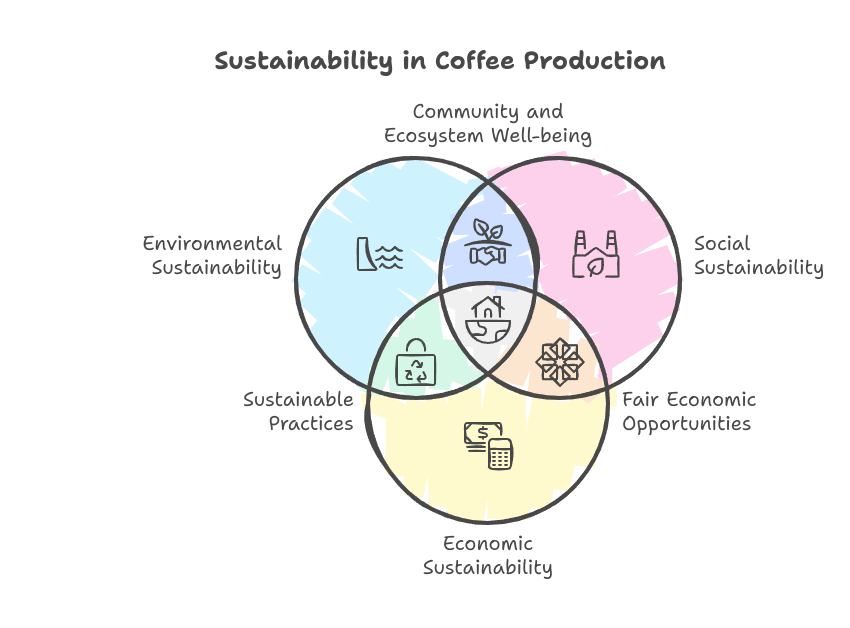
The Three Pillars of Sustainability
Sustainable coffee production is built on three interconnected pillars, each reinforcing the other:
- Environmental Sustainability: This focus is on protecting ecosystems, preserving biodiversity, and reducing coffee farming’s environmental footprint. This involves reducing deforestation, managing water resources, and minimizing the use of chemicals.
- Social Sustainability: Ensures that farmers and workers are treated fairly, receive decent wages, and work in safe conditions. It also promotes community development, healthcare, and education for farming families.
- Economic Sustainability: This aim is to provide stable and sufficient income for coffee producers, allowing them to invest in sustainable practices while maintaining their livelihoods.
When coffee is produced sustainably, it’s better for the planet and ensures long-term profitability and quality, creating a virtuous cycle of benefits for everyone.
The Environmental Impact of Conventional Coffee Farming
Unfortunately, not all coffee is produced sustainably. Conventional coffee farming practices can devastate the environment, leading to deforestation, soil degradation, and water pollution. Here are some of the critical environmental impacts of unsustainable coffee farming:
Coffee is often grown in tropical regions, home to some of the most biodiverse ecosystems on Earth. However, to meet global demand, vast forest areas are cleared to make room for coffee plantations. This deforestation not only destroys habitats for wildlife but also contributes to climate change by reducing the number of trees that absorb carbon dioxide.
Repeatedly planting coffee on the same land, especially in full-sun plantations, can lead to soil exhaustion. Over time, the soil loses fertility and the ability to support plant growth. Conventional coffee farming often relies on synthetic fertilizers to combat this issue, but these chemicals can further harm the soil and reduce its long-term productivity.
Coffee production is water-intensive, especially during the wet processing of beans. In regions where water is already scarce, this can strain local resources. Additionally, pesticides and fertilizers can contaminate water supplies, harm aquatic life, and reduce the availability of clean drinking water for nearby communities.
Sustainable Coffee Farming Practices
Sustainable coffee production employs various eco-friendly practices to combat the environmental damage caused by conventional farming. These methods reduce the ecological impact and improve the quality of the coffee produced.
Organic coffee farming avoids using synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides, relying instead on natural alternatives. This helps preserve soil health, protect local ecosystems, and reduce pollution. Organic farming often includes composting, crop rotation, and natural pest control.
In contrast to full-sun coffee plantations, shade-grown coffee is cultivated under the canopy of native trees. This practice mimics the natural environment in which coffee plants initially thrived. Shade-grown coffee helps preserve biodiversity, providing a habitat for birds, insects, and other wildlife. It also reduces the need for chemical inputs, as the natural ecosystem helps control pests.
Agroforestry is a farming approach that integrates coffee cultivation with other crops and trees, creating a more diverse and resilient ecosystem. This method improves soil health, prevents erosion, and promotes biodiversity. Agroforestry can also provide additional income for farmers by allowing them to grow food or timber alongside their coffee crops.
Sustainable coffee farms prioritize water conservation using drip irrigation, which minimizes water waste. Farms that process coffee beans through the natural (dry) method use significantly less water than the washed (wet) process. Sustainable farms also implement wastewater treatment systems to prevent pollution.
Fair Trade certification ensures that farmers are paid a fair price for their coffee, enabling them to invest in sustainable farming practices. Fair Trade standards also promote environmentally friendly practices, such as reducing chemicals and protecting biodiversity.
The Importance of Fair Trade and Direct Trade Coffee
Ethical sourcing is a crucial component of sustainable coffee production. Two key practices—fair Trade and Direct Trade—help ensure that coffee farmers are treated fairly and that sustainable practices are upheld.
Fair Trade coffee guarantees that farmers are paid a minimum price for their beans, protecting them from market fluctuations. This fair compensation is not just about money, it’s about respect and dignity. It enables farmers to invest in sustainable practices and improve their quality of life. In addition to financial support, Fair Trade also promotes safe working conditions, community development, and environmental sustainability.
Direct Trade involves a direct relationship between coffee roasters and farmers, cutting out intermediaries and providing greater transparency. With Direct Trade, roasters pay higher prices for premium-quality coffee, which allows farmers to earn more while incentivizing them to focus on sustainability and quality. The close relationship between roasters and farmers fosters innovation and collaboration, leading to more sustainable farming methods.
Both Fair Trade and Direct Trade contribute to the economic sustainability of coffee farming. By ensuring that farmers receive fair compensation, these practices help create stable incomes, allowing farmers to invest in better equipment, education, and sustainable farming methods.
Climate Change and Coffee: A Growing Threat
Coffee is susceptible to climate change. As global temperatures rise and weather patterns shift, coffee farmers face increasing challenges that threaten the future of coffee production.
Coffee plants thrive in specific temperature ranges, and even slight temperature increases can negatively impact yields. Higher temperatures can cause coffee cherries to ripen too quickly, resulting in lower-quality beans. Farmers in some regions already see reduced yields due to climate change.
Coffee plants rely on consistent rainfall to grow. However, climate change is causing erratic weather patterns, leading to droughts in some areas and flooding in others. Both extremes can damage crops and reduce production.
Warmer temperatures also create favorable conditions for pests and diseases like coffee leaf rust. This fungal disease can devastate coffee crops, particularly in Central and South America, where farmers have been battling outbreaks in recent years.
To combat the effects of climate change, scientists are developing climate-resilient coffee varieties. These new breeds are more resistant to extreme weather, pests, and diseases, ensuring the long-term viability of coffee production.
Certifications for Sustainable Coffee
When shopping for coffee, looking for certifications can help you make more informed and ethical choices. Here are some of the most widely recognized certifications for sustainable coffee:
As mentioned earlier, Fair Trade certification guarantees that farmers are paid fairly for their coffee. It also promotes sustainable farming practices, such as reducing chemical use and protecting biodiversity.
The Rainforest Alliance certification focuses on protecting ecosystems, wildlife, and human rights. Farms certified by the Rainforest Alliance must meet rigorous environmental and social standards, ensuring that coffee is produced sustainably.
Organic certification ensures coffee is grown without synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, or herbicides. This protects soil health, promotes biodiversity, and reduces pollution.
This certification is specific to shade-grown coffee that provides a habitat for migratory birds. Bird-friendly coffee is grown under a canopy of native trees, helping preserve forests and protect biodiversity.
The Social Impact of Sustainable Coffee Production
Sustainability isn’t just about the environment—it’s also about people. Sustainable coffee production can have a profound social impact by improving the lives of farmers and their communities.
Sustainable coffee production helps improve farmers’ livelihoods by paying fair wages and supporting ethical labor practices. This is especially important in developing countries, where many coffee farmers struggle to make a living.
Sustainable coffee initiatives often focus on empowering women, who play a vital role in coffee production. Programs that provide women with education, resources, and leadership opportunities help create more equitable and prosperous communities.
Sustainable coffee production supports community development by investing in healthcare, education, and infrastructure. This improves the quality of life for farmers and their families and strengthens the resilience of entire communities.
How to Make Sustainable Coffee Choices as a Consumer
As a consumer, you have the power to support sustainable coffee production by making informed choices. Here’s how you can make a difference:
When buying coffee, look for certifications like Fair Trade, Rainforest Alliance, Organic, and Bird-Friendly. These labels ensure that the coffee you’re purchasing was produced in an environmentally and socially responsible way.
You can also reduce your environmental footprint by minimizing waste. Use reusable coffee cups, filters, pods, and compost your coffee grounds. Additionally, seek out zero-waste coffee brands that prioritize eco-friendly packaging.
That prioritizes sustainability, ethical sourcing, and environmental stewardship. Many roasters and coffee companies are transparent about their supply chains and are committed to positively impacting the planet.
The Future of Coffee: Sustainability as a Necessity
The future of coffee depends on sustainability. As demand for coffee continues to grow, we must shift towards more sustainable production methods to protect the environment and farmers’ livelihoods.
The coffee industry faces significant challenges, including rising demand, climate change, and declining coffee yields. Sustainable production is essential to ensure that future generations can continue to enjoy coffee without depleting the planet’s resources.
Fortunately, innovations in sustainable coffee farming are providing new solutions. From climate-resilient coffee varieties to advances in organic agriculture and water conservation, these innovations are helping farmers adapt to changing conditions and produce coffee more sustainably.
Ultimately, consumers play a crucial role in shaping the future of coffee. By choosing sustainable coffee and supporting ethical brands, you can help drive positive change in the industry and ensure that coffee remains a viable crop for future generations.
Conclusion
Sustainable coffee production is not just about preserving the environment—it’s about creating a better future for farmers, communities, and coffee lovers worldwide. By making thoughtful coffee choices, you can help protect biodiversity, support ethical labor practices, and ensure that coffee remains a cherished part of our daily lives.
Next time you brew a cup of coffee, consider where it came from and the impact of your choice. Your coffee choices matter; together, we can create a more sustainable future for coffee production.






